How does OS Malevich update
The updating procedure is an integral part of the product development and improvement. Updates of Ajax hubs operating system increase the stability and security of the system, optimize its performance, ensure compatibility with new devices and expand the capability list.
The firmware updates only when the security system is disarmed.
The file size of the firmware does not exceed 0.5 MB.
The firmware downloading process runs in the background without affecting the functioning of the system.
The update installation takes less than 10 seconds.
The OS Malevich update is optional and can be disabled in the settings.
Hub Operating System Update
1. The hub determines if there is an update for operating system on the server
The firmware file for the hub is stored in the encrypted form on the Ajax Cloud server, and the server does not know the keys and the encryption method of the file. The access to the firmware database is provided only to a limited set of people in the company from the internal network of Ajax Systems. Since they have different levels of access, no one can make critical changes and sabotage the system. All actions are logged and monitored, and we know exactly who made the changes and when. Internal safety regulations prohibit the use of passwords to access the firmware database. SSH keys are used instead.
Hub connects to the server using the proprietary encrypted protocol. The authentication and verification system protects the server against forgery.
Hub checks for operating system updates every 5 minutes. If the automatic update option is enabled in hub settings, the hub updates automatically. If this option is disabled, the mobile app offers to install the update. If the security system is armed when hub detects a new firmware, the update is loaded in the background, not affecting the system operation at all, and installed after disarming the system.
Protection technologies:
Access to the firmware database by SSH keys only.
Access privileges and logging of changes to the server.
Server authentication and verification systems.
Using the proprietary encrypted communication protocol.
2. Transferring the update file from the server to the hub
Having detected the update file, the hub starts downloading the firmware to the external flash memory using any available communication channel with the server: Ethernet or GSM (and Wi-Fi for Hub Plus). The download is carried out in the background, not affecting the system operation.
Protection of the transmitted data between the hub and the server is provided by TLS combined with the security methods within the closed binary protocol.
Protection technologies:
TLS.
Using the proprietary encrypted communication protocol.
3. Checking the update file

Hub firmware is encrypted and signed with a checksum. If the firmware file is corrupted (intentionally or due to transmission errors), it is ignored, since the checksums will not match.
If the intruder corrupts the encrypted firmware file and substitutes the checksum, the checksum inside the decrypted firmware file will still not match the signature and the hub will reject the update file.
At most, the firmware file can be read from the external flash memory of the hub. However, the decryption of this file with the capabilities of modern computers will take thousands of years.
The firmware file includes a system of markers and properties that are checked before the installation. Information about them is available to a limited set of people to exclude the possibility of sabotage. If any marker or property fails validation, the update is canceled. Thus, the Hub will not install the firmware from the Hub Plus.
Protection technologies:
Verification of checksums, markers and properties.
Encryption.
4. Hub firmware update

During the update, the encrypted firmware file is read from the external flash memory of the hub by the bootloader, stored in the device microcontroller’s ROM.
The firmware is decrypted only inside the microcontroller, which cannot be accessed from the outside, therefore there is no possibility to read or substitute the firmware. Having decrypted the firmware file, the checksums are verified once more in order to make sure that no data was corrupted during the decryption process.
The bootloader inside the hub also controls the correct operation of the hub with a new firmware. If critical errors or malfunctions are detected, the hub deletes the corrupted firmware version and reflashes the latest stable release.
Only a limited set of people knows how the stable firmware is selected and how the correct operation is controlled, which complicates the sabotage. The bootloader itself is not updated, thereby excluding the possibility of sabotage of the firmware rollback mechanism.
Protection technologies:
Checksum verification after decryption.
Critical error control.
Control of correct operation of the hub with a new firmware.
After firmware update
The firmware update and the subsequent reboot of the hub takes less than 10 seconds. After that, hub reconnects to the server. The connection time depends on the number of active communication channels and does not exceed 30 seconds. Notifications about alarms and events are stored in the events feed even during the Hub update.
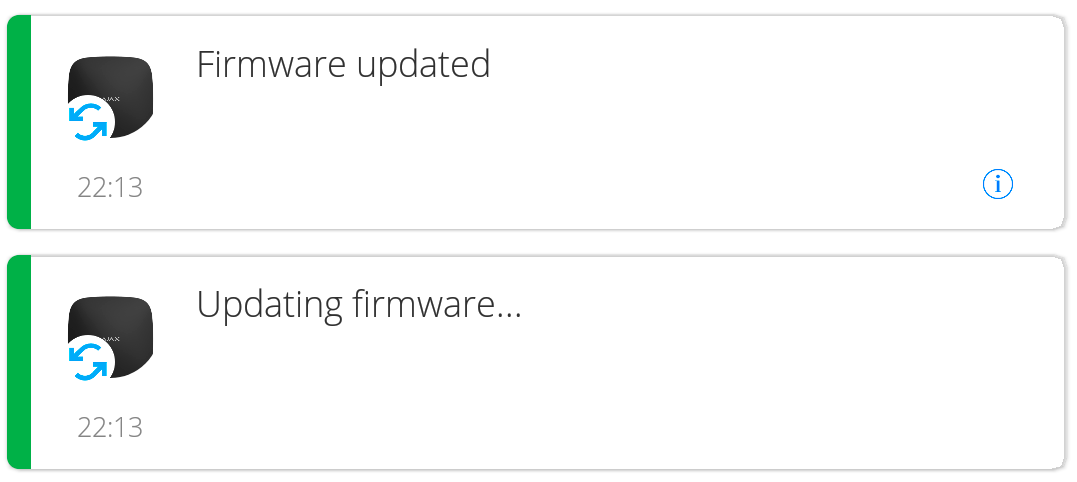
Ajax application display the following messages to inform about the start and the end of hub firmware update process:
The automatic update is optional and can be disabled. To do this, go to the service settings of the hub (Devices → Hub → Settings (⚙️) → Service) and disable “Firmware Auto-Update”.